Productive response and intestinal integrity of guinea pig (Cavia porcellus L.) fed Maize (Zea mays L.) forage inoculated with efficient microorganisms
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56926/repia.v1i2.21Keywords:
feeding, rhizospheric bacteria, guinea pigs, corn fodderAbstract
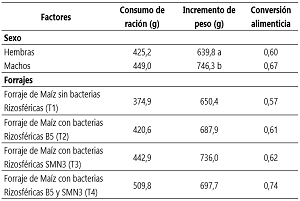
Livestock production aims to achieve greater productivity, using inputs in the feeding of species, which are cultivated with the least impact on the environment. The objective was to determine the best productive response and intestinal integrity of guinea pigs fed corn forage inoculated with efficient microorganisms. Forty-eight guinea pigs (24 males and 24 females), 50 days old, of the Peru breed with an average live weight of 450-550g were used. Ration consumption (g), weight gain (g), feed conversion, intestinal villus length (µm) and crypt depth (µm) were evaluated. The male guinea pigs obtained the highest ration consumption (449 g), the highest (P<0.05) weight gain (746.3 g) and the best feed conversion (0.6). In addition, they recorded the greatest intestinal villus length (0.507 µm) and crypt depth (0.141 µm). The treatment with maize forage inoculated with rhizospheric bacteria B5 and SMN3 obtained the highest weight increase (736 g). The most efficient feed conversion was evidenced by corn forage without inoculation of beneficial bacteria (0.57). In addition, this forage recorded a greater depth of the crypt.
Downloads
References
Montti, M. I., Visciglio, S. B., Raviol, F. H., Subovich, G. E., & Munitz, M. S. (2013). Incidencia de la carga inicial de pesticidas en fruta sobre los niveles residuales en aceites esenciales cítricos. Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, 24(47), 187–218. http://www.scielo.org.ar/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1851-17162013000200008
Pernía, B., Mero, M., Bravo, K., Ramírez, N., López, D., Muñoz, J., & Egas, F. (2015). Detección de cadmio y plomo en leche de vaca comercializada en la ciudad de Guayaquil, Ecuador. Revista Científica de Ciencias Naturales y Ambientales, 8(2), 81–86. https://revistas.ug.edu.ec/index.php/cna/article/view/221
Puente Flores, M., Rodriguéz Herrera, S., Gayosso Barragan, O., Mendoza Villarreal, R., & Oyervides García, A. (2016). Inoculación de bacterias diazotroficas en Genotipos de Maíz Forrajero. Revista Iberoamericana de Ciencias, 3(4), 37–44. http://www.reibci.org/publicados/2016/ago/1700104.pdf
Rodríguez-Hernández, M. G., Gallegos-Robles, M. Á., Rodríguez-Sifuentes, L., Fortis-Hernández, M., Luna-Ortega, J. G., & González-Salas, U. (2020). Cepas nativas de Bacillus spp. como una alternativa sostenible en el rendimiento de forraje de maíz. Revista Terra Latinoamericana, 38(2), 313–321. https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v38i2.690
Sánchez Laiño, A., Díaz Ocampo, R., Vega Pastuña, N., Godoy Becerra, S., & Sánchez Gallardo, S. (2009). Gramíneas tropicales en el engorde de cuyes mejorados sexados (Cavia Porcellus Linnaeus) en la zona de la maná. Ciencia y Tecnología, 2(1), 25–28. https://doi.org/10.18779/cyt.v2i1.78
Shiva, C., Bernal, S., Sauvain, M., Caldas, J., Kalinowski, J., Falcón, N., & Rojas, R. (2012). Evaluación de aceite esencialde oregáno (Origanum vulgare) y extracto deshidratado de jengibre (Zingiber officinale) como potenciales promotores de crecimiento en pollos de engorde. Revista de Investigaciones Veterinarias Del Perú, 23(2), 160–170. https://doi.org/10.15381/rivep.v23i2.896
Stephens, D. W., Brown, J. S., & Ydenberg, R. C. (2008). Foraging: Behavior and Ecology. Ilustrada.
Stringlis, I. A., Proietti, S., Hickman, R., Van Verk, M. C., Zamioudis, C., & Pieterse, C. M. J. (2018). Root transcriptional dynamics induced by beneficial rhizobacteria and microbial immune elicitors reveal signatures of adaptation to mutualists. The Plant Journal, 93(1), 166–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13741
Waliszewski, S. M., Herrero Mercado, M., & Cantú Martínez, P. C. (2008). Tejido adiposo: indicador de la contaminación por Plaguicidas organoclorados. Revista Salud Pública y Nutrición, 9(2), 2–6. https://respyn.uanl.mx/index.php/respyn/article/view/215
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Juvenal Napuchi-Linares, Christian Roker Flores-Guerra, José Virgilio Aguilar-Vásquez, William Celis-Pinedo , Jorge Cáceres-Coral , Laura Isabel Acosta-Mendoza

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain their rights:
a. The authors retain the intellectual property rights (copyright) of the published works, assigning to the journal the right of first publication.
b. Authors retain their trademark and patent rights, and also on any process or procedure described in the article.
c. Authors retain the right to share, copy, distribute, perform and publicly communicate the article published in REPIA (e.g., place it in an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in REPIA.
d. Authors retain the right to make a subsequent publication of their work, to use the article or any part of it (e.g., a compilation of their work, notes for conferences, theses, or for a book), provided they indicate the source of publication (authors of the work, journal, volume, number, and date).







