Nutritional requirements of macronutrients in stevia crop (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56926/repia.v2i2.49Keywords:
concentration, fertilization, nutrient extraction, stevia, yieldAbstract
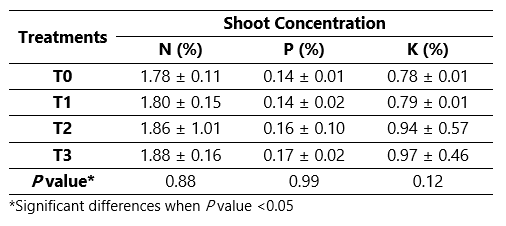
The stevia crop is native to America and has gained much popularity among consumers in the last decades; however, optimal nutrition and fertilization are required. Therefore, the objective of the present experiment aimed to determine the effect of fertilization on nutrient extraction and yield. Stevia plants were selected and propagated for field experiments. The study was installed in a randomized complete block design (RCBD) with four treatments: T0 (Control), T1 (10N-10P2O5-35K2O), T2 (80N-15P2O5-70K2O), T3 (160N-20P2O5-140K2O); With three repetitions each. The evaluation parameters were height, stem diameter, yield, nutrient concentration, and extraction (N, P, and K). ANOVA was performed, and the comparison of means by the Scott-Knott test (p≤0.05). The results indicated that the treatment with higher fertilizers was the best, indicating that larger doses are needed to reach an optimal value. The most required nutrient for stevia cultivation is nitrogen, followed by potassium and phosphorus, respectively. The crop extraction per ton was approximately 30 kg N, 4.4 kg of P2O5, and 18 kg of K2O for treatment with higher yield.
Downloads
References
Acosta, N. (2015). Las potencialidades de la stevia nacional en el mercado mundial. Observatorio de Economía Internacional.
Alcaraz Ariza, F. (2012). El factor suelo. Universidad de Murcia. https://www.um.es/docencia/geobotanica/ficheros/tema16.pdf
Brito Castrejón, H. (2018). Oportunidades para la agricultura en México: la estevia (Legislatur). Centro de Estudios para el Desarrollo Rural Sustentable y la Soberanía Alimentaria. https://portalhcd.diputados.gob.mx/PortalWeb/Micrositios/69e0b07c-5ceb-430c-8737-fa9d2e651750/92Estevia.pdf
Casaccia, J., & Álvarez, E. (2006). Recomendaciones técnicas para una producción sustentable del ka’a he’e (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni) en el Paraguay. Manual Técnico N° 8. Ministerio de Agricultura y Ganadería. Subsecretaría de Estado de Agricultura. Dirección de Investigación Agrícola.
Chamba Caillagua, K., & Merino Hidalgo, C. T. (2018). Respuesta del cultivo de stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni) a la fertilización orgánica bajo invernadero, en la estación experimental La Argelia [Universidad Nacional de Loja]. https://dspace.unl.edu.ec/jspui/handle/123456789/20573
EFSA. (2010). Scientific Opinion on the safety of steviol glycosides for the proposed uses as a food additive. EFSA Journal, 8(4). https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1537
Gómez-Merino, F. C., & Trejo-Téllez, L. I. (2015). Biostimulant activity of phosphite in horticulture. Scientia Horticulturae, 196, 82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.09.035
Harman, B. (2017). The Major Role of Phosphorus in Plant Growth and Productivity. IFA Cooperator, 83(2). https://grow.ifa.coop/agronomy/phosphorus-role-in-plant-growth-productivity
Jarma-Orozco, J., Combatt C., E., & Leguizamo, A. (2010). Aspectos nutricionales y metabolismo de Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni). Una revisión. Agronomia Colombiana, 28(2), 199–208. https://revistas.unal.edu.co/index.php/agrocol/article/view/18023
Katayama, O., Sumnida, T., Hayashi, H., & Mitsuhashi, H. (1976). The practical application of Stevia and research and development data (p. 747). I.S.U. Company.
Koo, W. (2017). Stevia Perú Exportación 2017 Octubre. AGRODATAPERU. https://www.agrodataperu.com/2017/11/stevia-peru-exportacion-2017-octubre.html
Lemus-Mondaca, R., Vega-Gálvez, A., Zura-Bravo, L., & Ah-Hen, K. (2012). Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, source of a high-potency natural sweetener: A comprehensive review on the biochemical, nutritional and functional aspects. Food Chemistry, 132(3), 1121–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.11.140
Lian, X., Xing, Y., Yan, H., Xu, C., Li, X., & Zhang, Q. (2005). QTLs for low nitrogen tolerance at seedling stage identified using a recombinant inbred line population derived from an elite rice hybrid. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 112(1), 85–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0108-y
Liao, H., Rubio, G., & Yan, X. (2001). Effect of phosphorus availability on basal root shallowness in common bean. Plant and Soil, 232, 69–79. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010381919003
Lima Filho, O. F., Malavolta, E., Sena, J. O. A., & Carneiro, J. W. . (1997). Absorção e acumulação de nutrientes em estévia Stevia rebaudiana (Bert.) Bertoni: I. Macronutrientes. Scientia Agricola, 54(1–2), 14–22. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90161997000100003
Liu, X., Ren, G., & Shi, Y. (2011). The effect of organic manure and chemical fertilizer on growth and development of Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni. Energy Procedia, 5, 1200–1204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2011.03.210
Patil, N. (2010). Biofertilizer Effect on Growth, Protein and Carbohydrate Content in Stevia rebaudiana Var Bertoni. Recent Research in Science and Technology, 2(10). https://updatepublishing.com/journal/index.php/rrst/article/view/522
Pérez Chamorro, O. B., & Calvache, M. (2018). Acumulación de nutrientes en Stevia Rebaudiana (Bertoni). Revista Alfa, 2(5), 82–89. https://doi.org/10.33996/revistaalfa.v2i5.40
Ramírez, J., Fernandez, Y., González, P., Salazar, X., Iglesias, J., & Olivera, O. (2016). Influencia de la fertilización en las propiedades físico-químicas de un suelo dedicado a la producción de semilla de Megathyrsus maximus. Pastos y Forrajes, 38(4). https://payfo.ihatuey.cu/index.php?journal=pasto&page=article&op=view&path%5B%5D=1856
Rodriguez, M., & Florez, V. (2004). Elementos Esenciales y Beneficiosos [Universidad de Almería]. http://hdl.handle.net/10835/3133
Salvador-Reyes, R., Sotelo-Herrera, M., & Paucar-Menacho, L. (2014). Study of Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni) as a natural sweetener and its use in benefit of the health. Scientia Agropecuaria, 157–163. https://doi.org/10.17268/sci.agropecu.2014.03.06
Taiz, L., & Zeiger, E. (2010). Plant Physiology (5th ed.). Sinauer Associates Inc.
Vera Peralta, C. D. (2016). Efecto de la fertilización nitrogenada en el cultivo de stevia (stevia rebaudiana bertoni) en la producción de materia seca bajo condiciones de San Martín [Universidad Nacional de San Martín]. http://hdl.handle.net/11458/600
Villalba Martínez, C., & Oroa Pfefferkorn, E. (2018). Concentración de nutrientes en tres variedades de stevia [Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) Bertoni] cultivadas en un Ultisol [Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología]. http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.14066/3735
Villanueva Avellaneda, K. (2009). Evaluación de cuatro niveles de fertilización orgánico mineral en el rendimiento de la yerba dulce (stevia rebaudiana bertoni) en la zona de Shucush (longar, amazonas) [Universidad Nacional del Centro del Perú]. http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12894/1912
Zetina Lezama, R., Vásquez Hernández, A., & Meneses Márquez, I. (2014). Aplicación de N-P-K para el establecimiento de Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni en suelos del centro de Veracruz. Revista Biológico Agropecuaria Tuxpan, 2(1), 19–24. https://doi.org/10.47808/revistabioagro.v2i1.240
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Juciksa Correa-Villacorta, Cesar Oswaldo Arévalo-Hernández, Juan Arévalo-Gardini, Enrique Arévalo-Gardini

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors retain their rights:
a. The authors retain the intellectual property rights (copyright) of the published works, assigning to the journal the right of first publication.
b. Authors retain their trademark and patent rights, and also on any process or procedure described in the article.
c. Authors retain the right to share, copy, distribute, perform and publicly communicate the article published in REPIA (e.g., place it in an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in REPIA.
d. Authors retain the right to make a subsequent publication of their work, to use the article or any part of it (e.g., a compilation of their work, notes for conferences, theses, or for a book), provided they indicate the source of publication (authors of the work, journal, volume, number, and date).







